Indian economic recovery a brief study

Introduction
The COVID-19 pandemic caused unprecedented disruption to economies worldwide. As countries implemented lockdowns and restrictions to control the spread of the virus, economic activities came to a standstill, resulting in significant GDP contractions across the globe. As we emerge from the pandemic, understanding the various recovery patterns becomes crucial for policymakers, businesses, and investors to make informed decisions.
This analysis explores the different economic recovery patterns that have emerged post-COVID and examines the strategies implemented by the Indian government to ensure sustainable growth, with a particular focus on the Atmanirbhar Bharat (Self-Reliant India) initiative.
Economic Recovery Patterns
Economists have identified several potential recovery patterns, each characterized by different trajectories of GDP growth following the initial economic shock. These patterns are typically represented by letters that visually resemble the recovery curve.
Option 1: Z-Shape Recovery
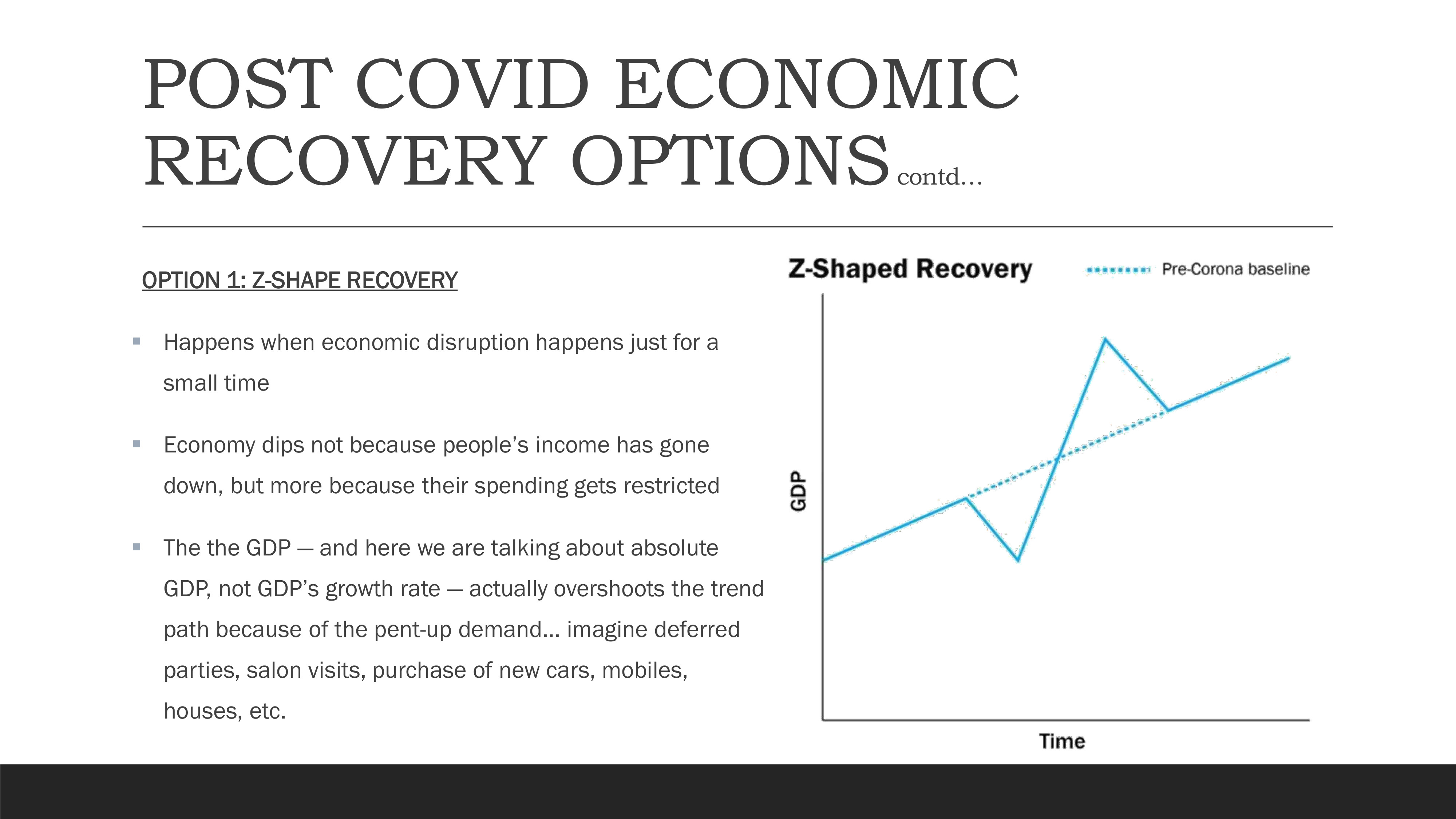
Z-Shape Recovery Pattern showing rapid return and overshoot
A Z-shaped recovery occurs when economic disruption happens for a short time. In this scenario, the economy dips not because people's income has decreased, but because their spending is restricted. Once restrictions are lifted, pent-up demand leads to a surge in spending, causing GDP to overshoot the trend path. This pattern is characterized by deferred consumption of goods and services like parties, salon visits, new cars, and housing.
Option 2: V-Shape Recovery
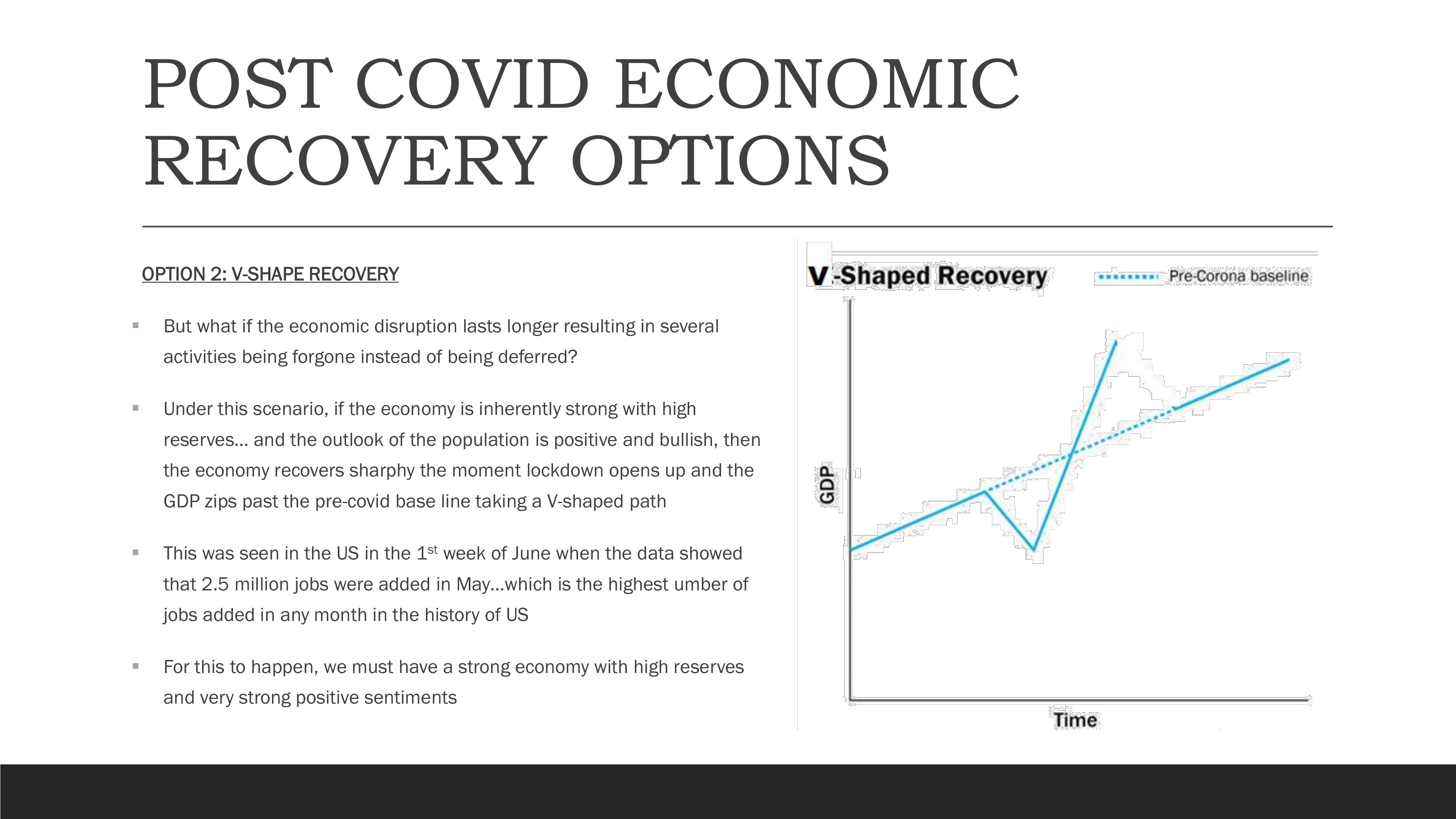
V-Shape Recovery Pattern showing sharp decline and rapid recovery
V-shaped recovery occurs when economic disruption lasts longer, resulting in several activities being forgone rather than just deferred. This pattern requires an inherently strong economy with high reserves and a positive, bullish outlook among the population. When lockdowns are lifted, the economy recovers sharply, with GDP quickly returning to and exceeding pre-COVID levels.
This pattern was observed in the US in early June 2020, when data showed that 2.5 million jobs were added in May—the highest number of jobs added in any month in US history. For a V-shaped recovery to occur, a strong economy with substantial reserves and very positive consumer and business sentiment is essential.
Option 3: U-Shape Recovery
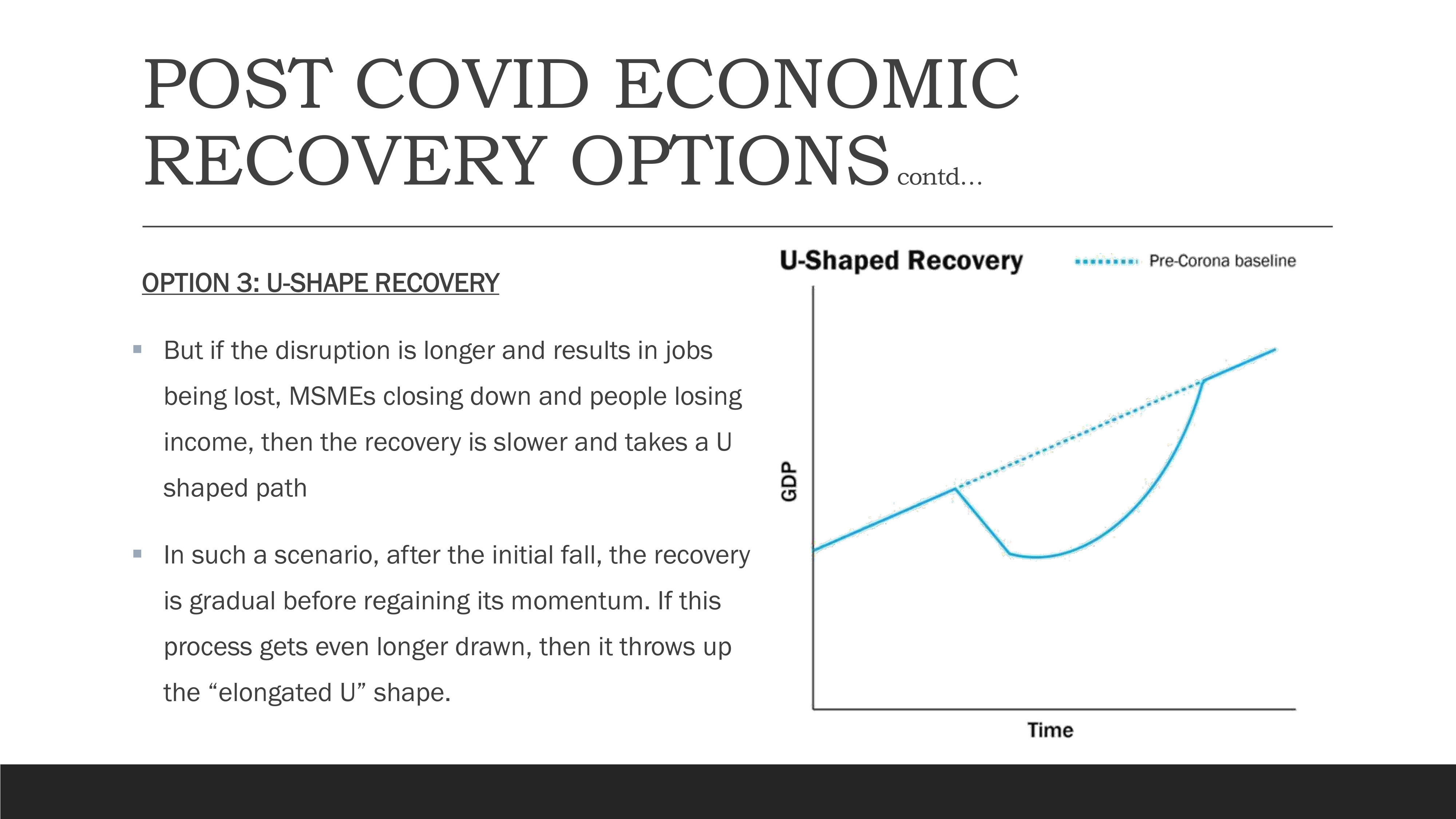
U-Shape Recovery Pattern showing prolonged bottom before recovery
When disruption is longer and results in job losses, MSME closures, and income reduction, recovery tends to be slower and follows a U-shaped path. After the initial fall, recovery is gradual before regaining momentum. If this process becomes more prolonged, it can result in an "elongated U" shape, indicating a more extended period of economic hardship before sustained growth resumes.
Option 4: W-Shape Recovery
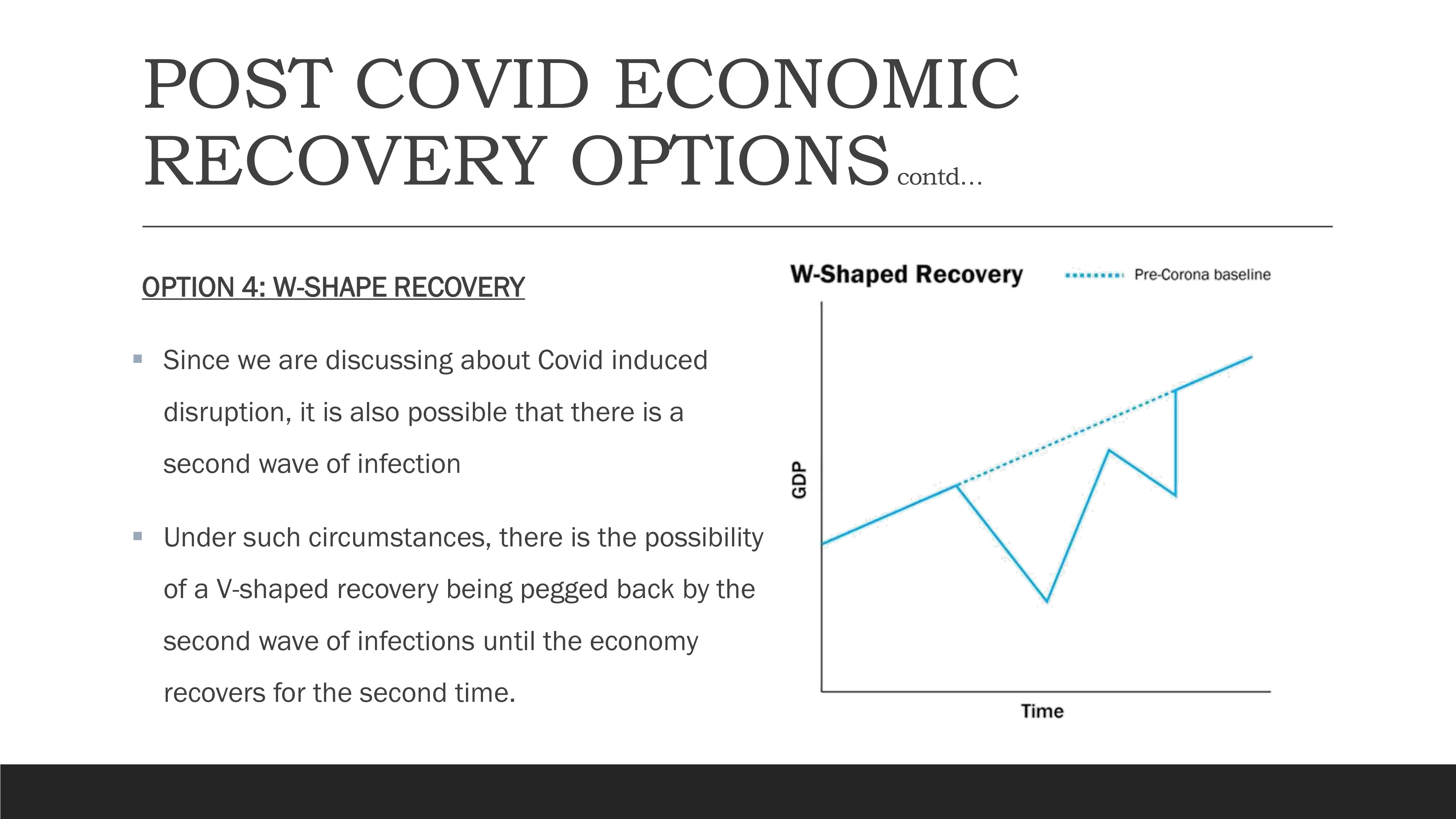
W-Shape Recovery Pattern showing double-dip recession
The W-shaped recovery becomes relevant when considering the possibility of subsequent waves of infection. In this scenario, an initial V-shaped recovery is interrupted by a second wave of infections, causing another economic downturn before a second recovery phase begins. This pattern represents a "double-dip" recession and recovery cycle.
Option 5: L-Shape Recovery
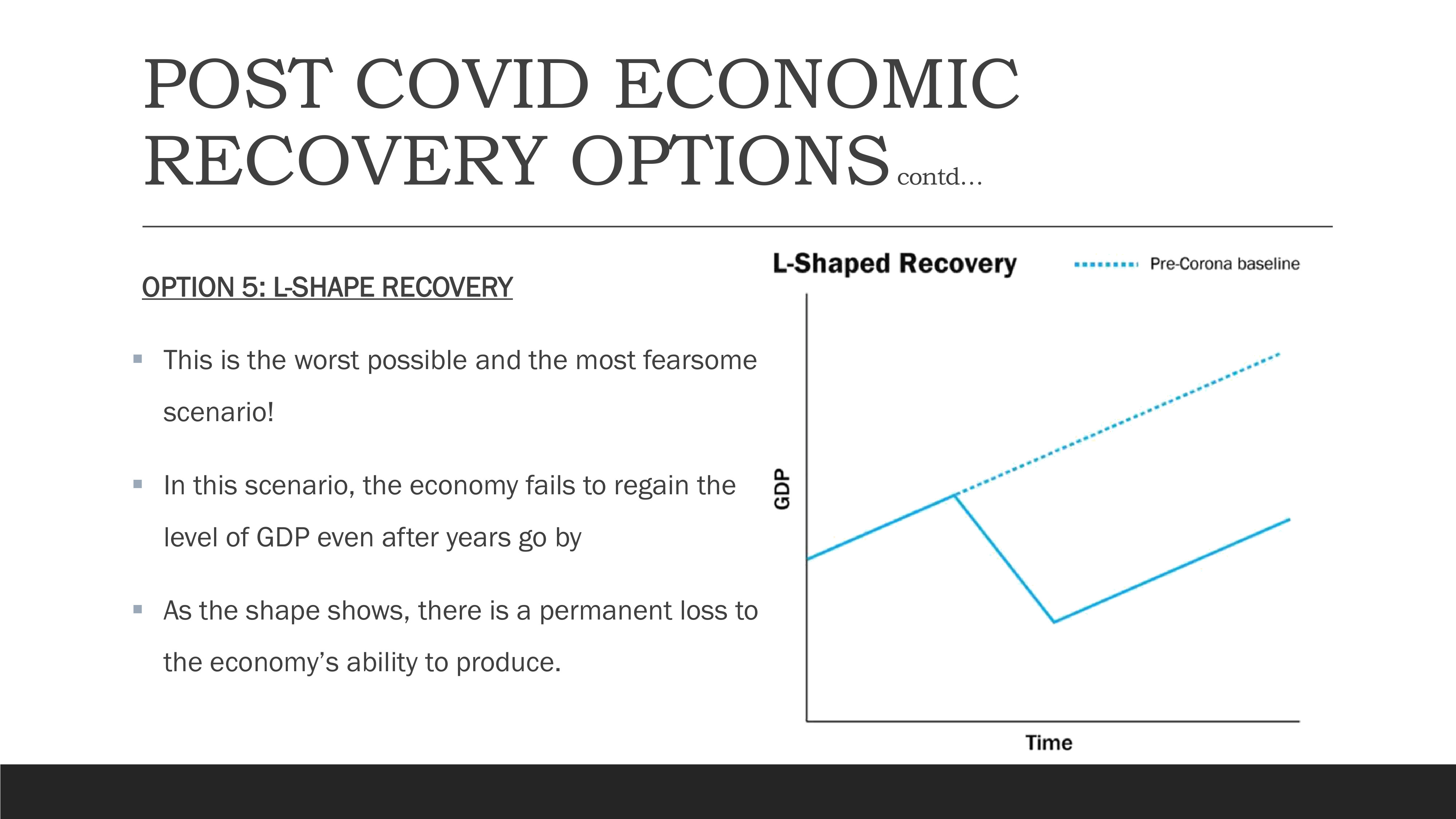
L-Shape Recovery Pattern showing permanent economic damage
The L-shaped recovery represents the worst-case scenario. In this pattern, the economy fails to regain its pre-crisis GDP level even after years have passed. The L-shape indicates a permanent loss to the economy's productive capacity, suggesting structural damage that prevents a return to the previous growth trajectory.
Guiding the Economic Recovery

Policy initiatives focused on guiding economic recovery
Effective policy initiatives are crucial for guiding economic recovery. Governments and industry must work together to implement strategies that address both immediate challenges and long-term growth objectives. These initiatives should focus on supporting vulnerable sectors, promoting investment, and enhancing economic resilience.
The Atmanirbhar Bharat Strategy
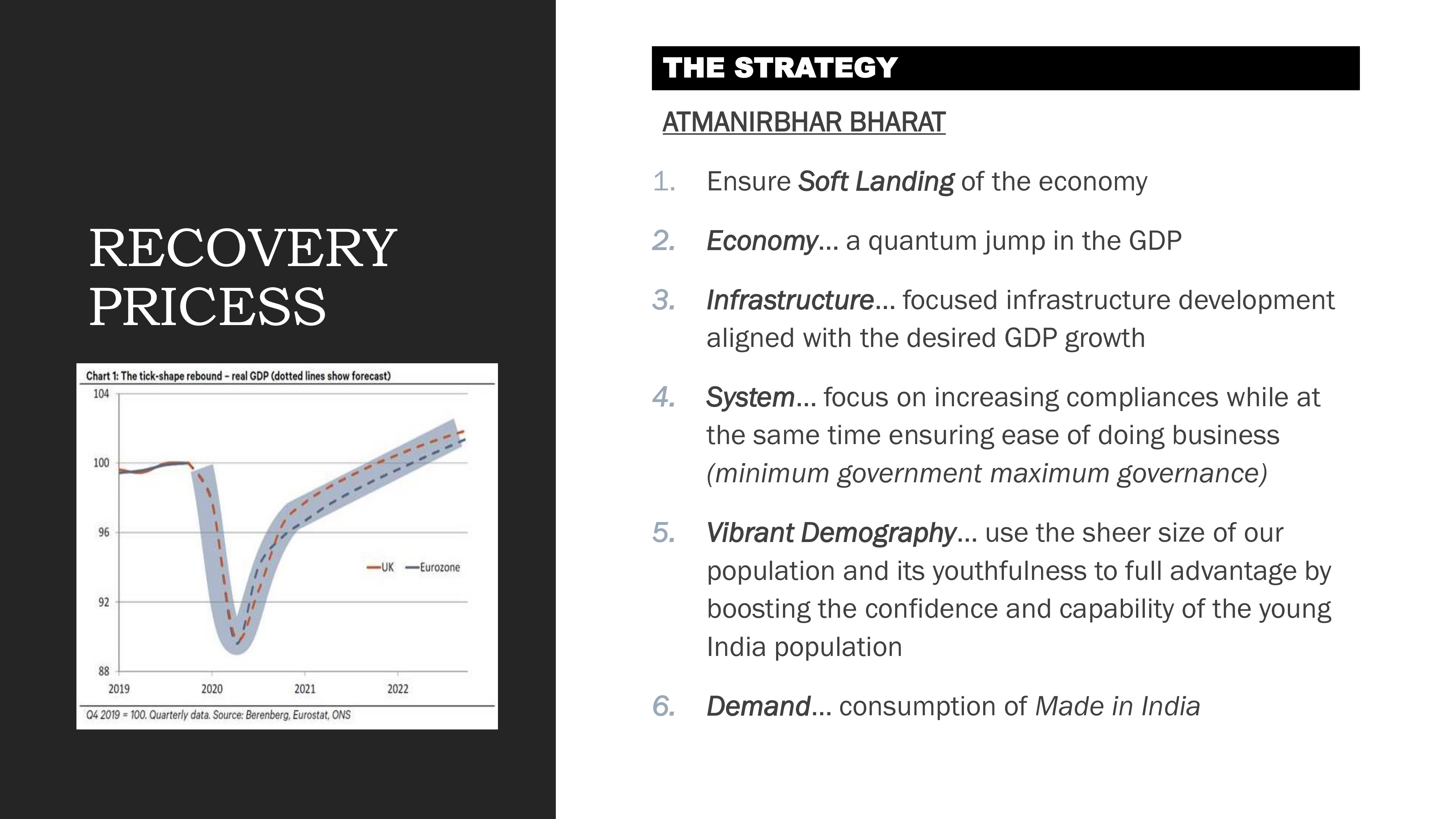
The six pillars of Atmanirbhar Bharat for economic recovery
India's response to the economic challenges posed by COVID-19 has been centered around the Atmanirbhar Bharat (Self-Reliant India) initiative. This comprehensive strategy consists of six key pillars:
- Ensure Soft Landing of the economy to minimize permanent damage
- Economy - Facilitating a quantum jump in GDP growth
- Infrastructure - Focused development aligned with desired GDP growth
- System - Increasing compliances while ensuring ease of doing business (minimum government, maximum governance)
- Vibrant Demography - Leveraging India's young population by boosting confidence and capability
- Demand - Promoting consumption of Made in India products
1. Ensuring Soft Landing of the Economy

Government initiatives to ensure business continuity
The first pillar focuses on ensuring that businesses, particularly MSMEs, can continue operations despite the economic shock. Key initiatives include:
- Redefinition of MSMEs to provide broader coverage of Indian industry
- Collateral-free automatic business continuity loans
- Equity support for stressed MSMEs through Rs 20,000 crore subordinate debt
- Fund of Funds for startup funding
- Restricting global tenders for government procurement up to Rs 200 crores
- Faster payment recovery cycle with mandatory 45-day payment terms for MSMEs
2. Economy - A Quantum Jump in the GDP

Strategies for achieving a quantum jump in GDP
The second pillar aims to catalyze significant GDP growth by leveraging India's strengths:
- Capitalizing on bumper crops from two consecutive years of good agricultural production
- Ensuring farmers receive fair prices for their produce despite abundance
- Boosting rural economy to increase disposable income among rural populations
- Channeling rural spending into urban retail, which in turn stimulates MSME manufacturing and services
The strategy emphasizes the importance of implementing Minimum Support Price (MSP) strictly to prevent price crashes due to abundant produce. Additionally, investments in storage facilities, irrigation infrastructure, productivity improvements, and crop insurance are recommended to protect farmers from uncertainties.
Conclusion
The path to post-COVID economic recovery will vary across countries depending on their economic structure, policy responses, and the effectiveness of pandemic containment measures. For India, the Atmanirbhar Bharat initiative provides a comprehensive framework for navigating the challenges and opportunities presented by the pandemic.
By focusing on supporting MSMEs, boosting rural income, investing in infrastructure, improving governance systems, leveraging demographic advantages, and stimulating domestic demand, India aims to achieve not just recovery but transformation toward a more resilient and self-reliant economy.
The success of these efforts will depend on effective implementation, continued policy support, and the ability to adapt strategies as the economic situation evolves. With the right approach, India can potentially emerge from the COVID-19 crisis with a stronger, more inclusive, and more sustainable economy.
Related Articles
Subscribe to Our Newsletter
Stay updated with our latest insights and industry trends.
Need Expert Economic Analysis?
Our team of experienced consultants can help your business navigate post-pandemic economic challenges and identify growth opportunities.